To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
How people discovered and studied the Earth
The first knowledge about the Earth goes back to the territory of the Ancient East - the inhabitants of Mesopotamia, Persia, Egypt, Phenicia. Occupations of the population: agriculture, cattle breeding, trade, settlement of peoples and wars increasingly expanded knowledge about the earth. Moving through deserts and sailing the seas, people learned to navigate by the Sun, Moon and stars. Ancient world
Herodotus An ancient Greek scientist, historian and traveler wrote a work - “History in Nine Books”.
Aristotle Ancient Greek philosopher, through research and observations of eclipses of the Moon and the Sun, concluded that the Earth is spherical.
Eratosthenes determined the diameter of the Earth. Wrote the book "Geography". He gave rise to the name of the science - geography.
860 - The Normans discovered the island of Iceland. 982 - The Normans discovered the island of Greenland. Around 1000 - The Normans discovered the eastern shores of North America. O. Iceland o. G R E N L A N D I A Middle Ages
Marco Polo 1271-1295 - The journey of the Italian merchant Marco Polo to China. He described the nature of the Pamirs, the monsoons of India, and learned a lot about the useful plants of China.
Afanasy Nikitin Afanasy Nikitin in the second half of the 15th century. He crossed Persia and the Arabian Sea and reached India, and compiled a detailed description of the countries.
The Portuguese expedition of B. Dias reached the southern tip of Africa, the Cape of Good Hope was discovered. 1487 - 1488
The German scientist Martin Beheim made a large globe. 1492
The first voyage of the Spanish expedition of H. Columbus and the discovery of the New World (America). 1492-1493
Vasco da Gama travels along the sea route around Africa and reaches the coast of India. 1497-1499
F. Magellan's first trip around the world. 1521 - 1524
1538 - Publication of a world map by the Flemish scientist G. Mercator.
Expedition to the northeastern regions under the leadership of V. Barents. 1594 - 1597
Sailing to the shores of Australia - the Dutch expedition of A. Tasman.
S. Dezhnev sailed from the Arctic Ocean to the Pacific. 1648 g
New time
Journey to Kamchatka by explorers V. Atlasov and L. Morozko. 1697-1699
Opening of the sea route from Kamchatka to North America. 1741
Circumnavigation of the English expedition by J. Cook.
The first Russian Antarctic expedition F.F. Bellingshausen and M.P. Lazarev
Drift of Fram Nansen in the Arctic Ocean. 1893 - 1896
Reaching the North Pole by F. Cook and R. Peary 1908 - 1909
R. Amudsen and R. Scott reached the South Pole.
Modern times 1932 The first through voyage along the Northern Sea Route on the icebreaking steamer Sibiryakov. 1937 Drift of the first station on the ice floe “North Pole” I.D. Papanina. 1955-59 The work of the Soviet expedition in Antarctica. 1957 - Launch of the first satellite. 1961 - Flight of the Vostok spacecraft
Over the past few centuries, we have made countless discoveries that have helped greatly improve the quality of our daily lives and understand how the world around us works. Assessing the full importance of these discoveries is very difficult, if not almost impossible. But one thing is for sure - some of them literally changed our lives once and for all. From penicillin and the screw pump to x-rays and electricity, here is a list of 25 of mankind's greatest discoveries and inventions.
25. Penicillin
If Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming had not discovered penicillin, the first antibiotic, in 1928, we would still be dying from diseases such as stomach ulcers, abscesses, streptococcal infections, scarlet fever, leptospirosis, Lyme disease and many others.
24. Mechanical watch
Photo: pixabay
There are conflicting theories about what the first mechanical watch actually looked like, but most often researchers adhere to the version that they were created in 723 AD by the Chinese monk and mathematician Ai Xing (I-Hsing). It was this seminal invention that allowed us to measure time.
23. Copernican heliocentrism
Photo: WP/wikimedia
In 1543, almost on his deathbed, Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus unveiled his landmark theory. According to the works of Copernicus, it became known that the Sun is our planetary system, and all its planets revolve around our star, each in its own orbit. Until 1543, astronomers believed that the Earth was the center of the Universe.
22. Blood circulation
Photo: Bryan Brandenburg
One of the most important discoveries in medicine was the discovery of the circulatory system, which was announced in 1628 by the English physician William Harvey. He became the first person to describe the entire circulatory system and properties of the blood that the heart pumps throughout our body from the brain to the tips of the fingers.
21. Screw pump
Photo: David Hawgood / geographic.org.uk
One of the most famous ancient Greek scientists, Archimedes, is considered the author of one of the world's first water pumps. His device was a rotating corkscrew that pushed water up a pipe. This invention took irrigation systems to the next level and is still used in many wastewater treatment plants today.
20. Gravity
Photo: wikimedia
Everyone knows this story - Isaac Newton, the famous English mathematician and physicist, discovered gravity after an apple fell on his head in 1664. Thanks to this event, we learned for the first time why objects fall down and why planets revolve around the Sun.
19. Pasteurization
Photo: wikimedia
Pasteurization was discovered in the 1860s by French scientist Louis Pasteur. It is a heat treatment process during which pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed in certain foods and drinks (wine, milk, beer). This discovery had a significant impact on public health and the development of the food industry around the world.
18. Steam engine
Photo: pixabay
Everyone knows that modern civilization was forged in factories built during the Industrial Revolution, and that it all happened using steam engines. The steam engine was created a long time ago, but over the last century it has been significantly improved by three British inventors: Thomas Savery, Thomas Newcomen, and the most famous of them, James Watt.
17. Air conditioning
Photo: Ildar Sagdejev / wikimedia
Primitive climate control systems have existed since ancient times, but they changed significantly when the first modern electric air conditioner was introduced in 1902. It was invented by a young engineer named Willis Carrier, a native of Buffalo, New York.
16. Electricity
Photo: pixabay
The fateful discovery of electricity is attributed to the English scientist Michael Faraday. Among his key discoveries, it is worth noting the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis. Faraday's experiments also led to the creation of the first generator, which became the forerunner of the huge generators that today produce the electricity we know in everyday life.
15. DNA
Photo: pixabay
Many believe that it was the American biologist James Watson and the English physicist Francis Crick who discovered it in the 1950s, but in fact this macromolecule was first identified in the late 1860s by the Swiss chemist Friedrich Maischer Miescher). Then, several decades after Maischer's discovery, other scientists conducted a series of studies that finally helped us clarify how an organism passes its genes to the next generation and how the work of its cells is coordinated.
14. Anesthesia
Photo: Wikimedia
Simple forms of anesthesia, such as opium, mandrake and alcohol, have been used by people for a long time, and the first mention of them dates back to 70 AD. But pain management moved to a new level in 1847, when American surgeon Henry Bigelow first introduced ether and chloroform into his practice, making extremely painful invasive procedures much more tolerable.
13. Theory of relativity
Photo: Wikimedia
Comprising Albert Einstein's two related theories, special and general relativity, the theory of relativity, published in 1905, transformed all of 20th century theoretical physics and astronomy and eclipsed Newton's 200-year-old theory of mechanics. Einstein's theory of relativity has become the basis for much of modern scientific work.
12. X-rays
Photo: Nevit Dilmen / wikimedia
German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen accidentally discovered X-rays in 1895 when he observed fluorescence produced by a cathode ray tube. For this pivotal discovery, the scientist was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1901, the first of its kind in the physical sciences.
11. Telegraph
Photo: wikipedia
Since 1753, many researchers have experimented with establishing long-distance communication using electricity, but a significant breakthrough did not come until several decades later, when Joseph Henry and Edward Davy invented the electrical relay in 1835. Using this device they created the first telegraph 2 years later.
10. Periodic table of chemical elements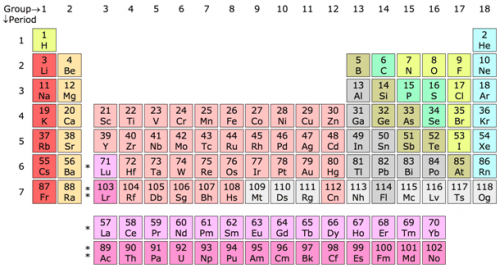
Photo: sandbh/wikimedia
In 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that if chemical elements are ordered by their atomic mass, they tend to form groups with similar properties. Based on this information, he created the first periodic table, one of the greatest discoveries in chemistry, which was later called the periodic table in his honor.
9. Infrared rays
Photo: AIRS/flickr
Infrared radiation was discovered by British astronomer William Herschel in 1800 when he studied the heating effect of different colors of light, using a prism to separate the light into a spectrum, and measuring the changes with thermometers. Today, infrared radiation is used in many areas of our lives, including meteorology, heating systems, astronomy, tracking heat-intensive objects and many other areas.
8. Nuclear magnetic resonance
Photo: Mj-bird / wikimedia
Today, nuclear magnetic resonance is continually used as an extremely accurate and effective diagnostic tool in the medical field. This phenomenon was first described and calculated by American physicist Isidor Rabi in 1938 while observing molecular beams. In 1944, the American scientist was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery.
7. Moldboard plow
Photo: wikimedia
Invented in the 18th century, the moldboard plow was the first plow that not only dug up the soil, but also stirred it, making it possible to cultivate even very stubborn and rocky soil for agricultural purposes. Without this tool, agriculture as we know it today would not exist in northern Europe or central America.
6. Camera obscura
Photo: wikimedia
The forerunner of modern cameras and video cameras was the camera obscura (translated as dark room), which was an optical device used by artists to create quick sketches while traveling outside their studios. A hole in one of the walls of the device served to create an inverted image of what was happening outside the chamber. The picture was displayed on the screen (on the wall of the dark box opposite the hole). These principles have been known for centuries, but in 1568 the Venetian Daniel Barbaro modified the camera obscura by adding converging lenses.
5. Paper
Photo: pixabay
The first examples of modern paper are often considered to be papyrus and amate, which were used by ancient Mediterranean peoples and pre-Columbian Americans. But it would not be entirely correct to consider them real paper. References to the first production of writing paper date back to China during the reign of the Eastern Han Empire (25-220 AD). The first paper is mentioned in chronicles dedicated to the activities of the judicial dignitary Cai Lun.
4. Teflon
Photo: pixabay
The material that keeps your pan from burning was actually invented completely by accident by American chemist Roy Plunkett when he was looking for a replacement refrigerant to make household life safer. During one of his experiments, the scientist discovered a strange, slippery resin, which later became better known as Teflon.
3. Theory of evolution and natural selection
Photo: wikimedia
Inspired by his observations during his second voyage of exploration in 1831-1836, Charles Darwin began writing his famous theory of evolution and natural selection, which, according to scientists around the world, became a key description of the mechanism of development of all life on Earth
2. Liquid crystals
Photo: William Hook / flickr
If the Austrian botanist and physiologist Friedrich Reinitzer had not discovered liquid crystals while testing the physicochemical properties of various cholesterol derivatives in 1888, today you would not know what LCD televisions or flat-panel LCD monitors are.
1. Polio vaccine
Photo: GDC Global / flickr
On March 26, 1953, American medical researcher Jonas Salk announced that he had successfully tested a vaccine against polio, a virus that causes a severe chronic disease. In 1952, an epidemic of the disease diagnosed 58,000 people in the United States and claimed 3,000 innocent lives. This spurred Salk on a quest for salvation, and now the civilized world is safe at least from this disaster.
Knowledge about the Earth, continents, oceans and seas did not come to people right away. They accumulated little by little over many centuries and were systematized by many geographers and navigators.
Nowadays, with the help of satellites, you can easily photograph and explore any corner of our vast planet. However, this was not always the case. People have spent a lot of effort and time in order to open the world.
The first explorers
In the ancient world, the first discoveries of new lands were associated with the construction of trade routes by sailors - merchants. In 600 BC, the ancient Phoenicians were able to travel around Africa for the first time in human history, which enabled people to draw the first geographical maps of the continent.
During this sea voyage, islands such as Madeira, the Azores and the Canary Islands were discovered. Another heroic discoverer of the world was the ancient Greeks, who managed not only to discover such lands as India, the south of France, the southwestern lands of Britain, Greenland, but also to draw correct conclusions regarding natural phenomena and the structure of the planet.
It was the ancient Greek navigators who first proposed the theory that the earth was round in shape. The ancient Greeks, who traveled through the northern lands, spoke in their state about the northern lights, about the breath of the sea (high and low tides), but their compatriots took them for madmen, their stories sounded so implausible.
Great geographical discoveries
Thanks to the development of trade and the improvement of shipbuilding, in the 15-17th century the period of Great Geographical Discoveries began in Europe, during which people managed to discover continents and islands that until then had remained under a veil of secrecy.
In 1492, the famous Spanish navigator Christopher Columbus, in search of new trade routes with India, discovered the New World, which later received the name America. A significant contribution to the discovery of new territories was made by the Portuguese sailor Vasco de Gamma, who in 1948 discovered several islands in Asia and Oceania.
In 1512, the Portuguese Ferdinand Magellan made the first trip around the world. During this voyage the first maps of the Indian Ocean were made.
In the 17th century, Europeans discovered New Zealand, the Hawaiian Islands and Australia. During the same period, Russian pioneers conquered the entire territory of Siberia and entered the Far East.
The last continent that people discovered in 1820 was distant Antarctica.
The importance of geographical discoveries
As a result of the fact that people discovered new lands, humanity was able to accumulate knowledge about the world order: the movement of the sun, the moon, the change of seasons in different territories, the presence of poles.
The benefits and natural resources that abounded in the new lands became available to people. Thanks to geographical discoveries during Antiquity, the Middle Ages and the Modern Age, we have the opportunity to fully study the geography of our planet.




 -Set the diameter of the Earth. - Wrote the book “Geography”. -Introduced the word “geography” into use. - Identified territories that differ from each other in natural conditions, characteristics of life and way of life of the population. - Made a map of the inhabited land (ecumene).
-Set the diameter of the Earth. - Wrote the book “Geography”. -Introduced the word “geography” into use. - Identified territories that differ from each other in natural conditions, characteristics of life and way of life of the population. - Made a map of the inhabited land (ecumene).
 The ancient Greek philosopher, through research and observations of eclipses of the Moon and the Sun, concluded that the Earth is spherical.
The ancient Greek philosopher, through research and observations of eclipses of the Moon and the Sun, concluded that the Earth is spherical.
 The important work of Ptolemy “Geography” in 8 volumes is a collection of knowledge about the geography of everything known to the ancient peoples of the world. Ptolemy was a proponent of mathematical geography, and his work is a detailed guide to compiling an atlas of the world, indicating the exact coordinates of each point. He laid the foundations of regional studies and also listed about 8,000 geographical names.
The important work of Ptolemy “Geography” in 8 volumes is a collection of knowledge about the geography of everything known to the ancient peoples of the world. Ptolemy was a proponent of mathematical geography, and his work is a detailed guide to compiling an atlas of the world, indicating the exact coordinates of each point. He laid the foundations of regional studies and also listed about 8,000 geographical names.

 Ibn Battuta (1304–1377), Arab traveler, wandering merchant. Over the course of twenty-nine years, he covered a distance of 117,000 kilometers, visiting Northern and Western Africa, Southern and Southeastern Europe (including the territory of today's Russia and Ukraine), the Middle East, India and China, Sumatra, Ceylon and the Maldives, while visiting many countries. Ibn Battuta described all the countries he visited as completely as possible.
Ibn Battuta (1304–1377), Arab traveler, wandering merchant. Over the course of twenty-nine years, he covered a distance of 117,000 kilometers, visiting Northern and Western Africa, Southern and Southeastern Europe (including the territory of today's Russia and Ukraine), the Middle East, India and China, Sumatra, Ceylon and the Maldives, while visiting many countries. Ibn Battuta described all the countries he visited as completely as possible.

 The Normans discovered the island of Iceland, then the island of Greenland, and in the 9th century they reached the shores of North America.
The Normans discovered the island of Iceland, then the island of Greenland, and in the 9th century they reached the shores of North America.
 1271 -1295 The journey of the Italian merchant Marco Polo to China. He described the nature of the Pamirs, the monsoons of India, and learned a lot about the useful plants of China.
1271 -1295 The journey of the Italian merchant Marco Polo to China. He described the nature of the Pamirs, the monsoons of India, and learned a lot about the useful plants of China.
 In the second half of the 15th century. He crossed Persia and the Arabian Sea and reached India, and compiled a detailed description of the countries.
In the second half of the 15th century. He crossed Persia and the Arabian Sea and reached India, and compiled a detailed description of the countries.
 1487 - 1488 The Portuguese expedition of B. Dias reached the southern tip of Africa, the Cape of Good Hope was discovered.
1487 - 1488 The Portuguese expedition of B. Dias reached the southern tip of Africa, the Cape of Good Hope was discovered.


 Vasco da Gama travels along the sea route around Africa and reaches the coast of India. 1497 - 1499
Vasco da Gama travels along the sea route around Africa and reaches the coast of India. 1497 - 1499





 The significance of the Great Geographical Discoveries Scientific Practical Socio-political Approval of the idea Improved The world was divided into spherical Earths, ancient maps; The Old and New unity of the World created the first globe, the Light of the Ocean; development of navigational instruments for cartography (compass, gnomon, geography and other astrolabes); Sci. Description of the discovery of new and different territories of land deposits, the World Ocean, people's lives Universal (humanistic) The world is populated by diverse peoples, each with their own culture, customs, traditions that should be respected in order to achieve mutual understanding and exchange goods
The significance of the Great Geographical Discoveries Scientific Practical Socio-political Approval of the idea Improved The world was divided into spherical Earths, ancient maps; The Old and New unity of the World created the first globe, the Light of the Ocean; development of navigational instruments for cartography (compass, gnomon, geography and other astrolabes); Sci. Description of the discovery of new and different territories of land deposits, the World Ocean, people's lives Universal (humanistic) The world is populated by diverse peoples, each with their own culture, customs, traditions that should be respected in order to achieve mutual understanding and exchange goods
 1741 Opening of the sea route from Kamchatka to North America.
1741 Opening of the sea route from Kamchatka to North America.

How people discovered the world
Objective of the lesson:
To become familiar with how people's ideas about the shape and nature of the Earth have changed over time;
How did people's knowledge about nature develop?

Equipment:
Physical map of the hemispheres
Demonstration tables about the idea of the Earth in ancient times
Video “The History of Geographical Discoveries” (or messages)

Lesson Plan
Homework review
Primitive people and nature
World of Ancient Civilizations
Middle Ages
Christopher Columbus
Ferdinand Magellan, Juan Sebastian de Elcano
Francis Drake
Lesson summary
Homework

Homework review
What is geography?
Who was the first to formulate the concept of geography?
What types of geographies do you know?
Checking weather calendars

Learning new material
Messages or film "The History of Geographical Discovery" are used
During performances (or watching a film), students fill out the table:
MAIN STAGES IN THE ACCUMULATION OF KNOWLEDGE ABOUT THE EARTH
Stages Time Names of famous Result
travelers of discovery

Primitive people and nature
Ancient people are one of the biological components
Man has had minimal impact on nature (limit of material resources)
Man studied nature to survive

World of Ancient Civilizations
The starting point for the existence of geography and other sciences
Writing, religion, cities appear
Communication between residents of different territories
The era of sea travel (Which seas did they travel across?)
A question arose about the shape of the Earth (What were the ideas?)

Middle Ages
Longer journeys are made (improvement of technology and shipbuilding) - access to the ocean
Travel began to have a scientific and economic character
There are assumptions about the sphericity of the Earth

Christopher Columbus
http://www.vokrugsveta.ru/encyclopedia/index.php?title=%D0%98%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B6%D0%B5 %D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5:Colombo.jpg

Columbus's voyage routes "Big Encyclopedia of Cyril and Methodius - 2005"

"PINTA", "NINA" AND "SANTA MARIA"- the ships on which Christopher Columbus made his first voyage to the shores of America
IGDA/G. Dagli Orti

Monument to Columbus in Barcelona (Spain)

Columbus name on the world map
The state of Columbia, the federal district of the United States, and numerous geographical features of America bear the name of Columbus.

Ferdinand Magellan
M AGELLAN (Magallanes) (Spanish: Magallanes) Fernand (1480-1521), navigator whose expedition completed the 1st circumnavigation of the world. Born in Portugal.

Magellan's caravels

Modern model of Magellanic carrack "Victoria".

Juan Sebastian Elcano
Every four years, the Spaniards pay tribute to the memory of Juan Elcano by organizing a holiday with historical reconstruction.
The schooner “Juan Sebastian de Elcano” is named after the associate of Magellan, who completed the first expedition around the world.

Sanlúcar Antonio Pigafetta
Of the five ships that sailed from Spain, only the Victoria returned to Sanlúcar near Cadiz (September 6, 1522). There were only 18 sailors on board (out of the 265 who left Spain with Magellan). Among the survivors was Antonio Pigafetta, who compiled the famous description of the historical journey.

Antonio Pigafetta
Born approx. 1491, in the city of Vicenza, died after 1534, ibid.) - Italian navigator, participant in the Magellan-Elcano expedition (1519–22). During the first voyage around the world, he kept diaries, which he presented to Emperor Charles V.

Ferdinand Magellan
In 1519-21 he led a Spanish expedition to find a western route to the Moluccas.

He discovered the entire coast of South America south of La Plata, circumnavigated the continent from the south, discovered the strait named after him, and the Patagonian Cordillera; first to cross the Pacific Ocean. (1520), having discovered Fr. Guam, and reached the Philippine Islands, where he was killed in a battle with local residents.

Ferdinand Magellan
Magellan proved the existence of a single World Ocean and provided practical evidence of the sphericity of the Earth. The voyage was completed by J. S. Elcano, who circumnavigated Africa from the south

Named after Magellan
Named after Magellan
Magellanic clouds
Strait of Magellan
The Magellan Seamount in the Pacific Ocean, near the Marshall Islands.

From the book "Big Electronic Children's Encyclopedia"
Fernando Magellan

Material from Wikipedia - the free encyclopedia
Magellanic clouds- satellite galaxies of the Milky Way. Visible to the naked eye in the Southern Hemisphere. Named after Ferdinand Magellan, who first saw them in 1519 during his trip around the world.

Strait of Magellan
Strait of Magellan- the strait separating continental South America and the Tierra del Fuego archipelago is narrow (minimum width 2.2 kilometers) and in some places very dangerous for navigation. The length of the strait is 575 kilometers, the smallest depth in the fairway is 20 meters.

Strait of Magellan
17th century map

Francis Drake
The honor of being the first commander of a round-the-world sea expedition to reach Europe to Europe across three oceans alive and unharmed belongs to the Englishman Sir Francis Drake (1541 - 1597).
Young polymath – Geography and discoverers

Magellan's Cross. Philippines. Cebu.

High-tech original watch Magellan 1521 (Magellan company) is made in the shape of an ancient marine compass, the dial of which is similar to a globe. “1521” is the year the famous navigator Magellan completed his first voyage around the world. The dial is protected by a sapphire dome, resistant to shocks and scratches.

Lesson summary
We found out that knowledge about the planet has accumulated throughout human history
Travel and historical discoveries expanded people's knowledge about planet Earth

Homework
Answer the questions § 2
Plot the most important travel routes on a contour map

Homework for the curious
He spent more than 30 years hiking and sailing. The development of the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the east of the Indigirka and Kolyma rivers is associated with his name. With his satellites, he for the first time circled the eastern tip of Asia and discovered the strait separating Asia from America. But his report and report on the voyage around the Chukotka Peninsula lay in the Yakut archive for more than 80 years and was discovered only during the Great Northern Expedition. 250 years after the voyage, his name was immortalized on the map.


